The ISO 9000 series of standards was developed and introduced by the “International organization for Standardization”. ISO 9001 is most well knowing standards ever, because millions of organizations across the world implemented its system in line with ISO 9001 requirements. it is assist the point organizations to implement quality management, off course it is for “quality of a product” as expecting every business and its customers to ensure that its products or services gives fully satisfaction to the customers’ end applications and customer chain. This standard also most popular because its generic standards can apply in any scale of organization whatever product / services, how much scope of processes and activities.
Quality management mean:
- Products meet the key objectives
- Customer Satisfaction improve
- Compliances of regulations
- Continual improvement
8 Quality Management Principles:
- Customer focus: Understand Regular and future customer requirements – explicit & implicit, Measure customer satisfaction, Implement plans means to meet these requirements and establish continually improved satisfaction.
- Leadership: Establish vision, provide direction and share values, set challenging targets & implement strategies to achieve these targets, coach, facilitate and empower peoples across organization.
- Engagement of people: Create control of departmental goals and organizational policy. Use knowledge and experience in operational decisions.
- Process approach: Identification of scope of a set of organizational activity, identify supplier and customer inputs and outputs include external and internal.
- System Approach to management: Establishment of inter connection of processed starting identification of customer requirements to delivery of product and post-delivery till use of product.
- Continual Improvement: Measurement parameters, Analysis of performance, provide opportunities, tools and encouragement to contribute to continual improvement.
- Evidence-based decision making: Identify processes and activities which will provide measureable data information, set mechanism for analyzing data and analyze information with reference to planned targets and goals. Eliminate non-significance addition activities like reduce rework, improve machine efficiency, reduce wastage, reduce inventory and its transportation, reduce process cycle time.
- Relationship management: Creating relationship & assured suppliers for their participation in development of product, processes and system.
General QMS (Quality Management System) ISO 9001 Awareness
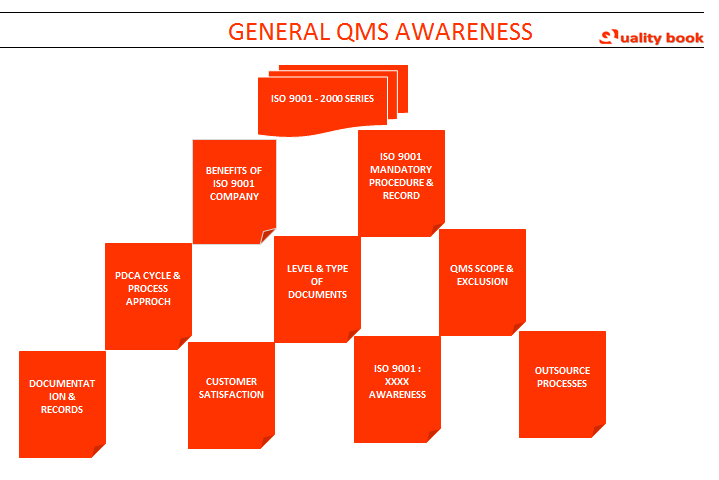
Benefits of quality management system – ISO 9001
| INTERNAL BENEFITS |
|---|
Improvements
Reductions
|
| EXTERNAL BENEFITS |
Improvements
Reductions
|
Quality Management System – Levels of Documentation
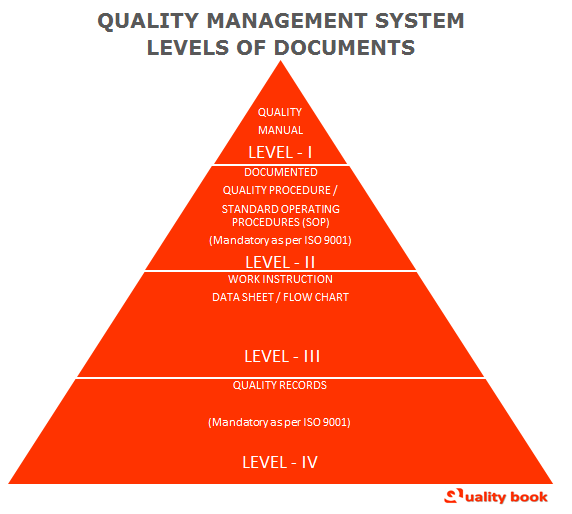
Above pyramid explains the Levels of quality management system, how to implement quality management system in the organization. Mostly organization used the international standard by internal and external parties including certification bodies to evaluate the organizatio’s ability to meet customer, statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to product and organizatio’s internal requirements.
How to implement ISO 9001 – Quality management system in organization?
- Very first step of the implementation of ISO 9001 – quality management system in organization, you have to compare your existing quality system with ISO 9001 requirements, take the outsource feedback like customers and suppliers on the current quality management.
- Prepare the team for establishment and implementation, define roles and responsibility and create road map for adapting the ISO 9001 standard requirements.
- Employee involvement is very important so motivate employee to get involve with activities and training.
- Take the Grip on the 8 quality management principle for your ISO 9001 system implementation.
- To ensure your system on track and continually improving by reviews your ISO 9001 system.
- Review your ISO 9001 system: (1) Quality Manual (Level – I) (2) Quality Objectives & company objectives (3) Quality Policy (4) Quality Procedures / Standard Operating Procedures (Level – II) (5) Work Instructions (Level – III) (6) Records & Forms – Documentation (Level – IV)
- Take the support of the metrics, charts and other tools that helps to shows quality management system performance in measureable figures.
- Conduct Management review meeting as per internal standards requirements and discuss possible all the points, targets, and achievements.
- Perform internal audits once in quarter are recommended by internal auditors.
Type of Audits
| SR.NO | FEATURES | 1ST PARTY AUDIT | 2ST PARTY AUDIT | 3ST PARTY AUDIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Definition | Conducted by OR on behalf of the organization itself- for internal purpose & can form the basis for an organization’s self-declaration of conformity. | Conducted by customer of the organization OR By other persons on behalf of the customer. | Conducted by external independent organizations. Such organizations usually accredited. Provide certification OR Registration of conformity with requirements such as those of ISO 9001. |
| 02 | Purpose | To asses effectiveness of Quality Management system | To asses effectiveness of Quality Management system | To seek conformance of ISO 9001. |
| 03 | Audit Conducted By | Qualified Internal Auditor. | Techno commercial team. (Quality assurance +Purchase) | Qualified auditor’s from certified agency. |
| 04 | Authorized By | Top Management | Customer top management | Top management supplier/customer |
| 05 | Audit planning & Preparation | Management Representative | Techno commercial team member | Lead Auditor |
| 06 | Report Submission | Management Representative | Management Representative / Quality Assurance / Top management | Management Representative /Accreditation body |
Various Stage of Audit:
- Adequacy audit: An Implementation, which decides the level documented system represented by quality manual and it is associated procedure adequately meet the requirement of the applicable standards.
- Compliance Audit: An audit which seek to establish the extent to which the documented system is implemented & observed by the workforce.
- Surveillance Audit: Having issued a certificate, the certificate body would have some system of monitoring the organization to ensure continued compliance with the standard. Generally, issues are identified in system are: (1) Last Audit Finding (2) Internal Audit and its results (3) Management Reviews (4) Customer Satisfaction Ratio & Complaints (5) Objective Analysis (6) Non-conformance & Corrective, Preventive Actions (7) Change in Quality manuals & supporting Documents (8) Continual Improvement