What is Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)?
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) : A process which use a multidisciplinary approach to recognize and evaluate the potential failure of a product/process and the effects of that failure.
This process will be follow by the identification of preventive action that can be eliminate or reduce the chance of the potential failure occurring.
In casual use “FMEA” also means “Failure modes and effects Criticality Analysis (FMECA)”. FMEA Is proactive analysis tool support to anticipate failure modes even before any occurrences as well as possible to prevent the negative effects of these failures modes from reaching the customers before new product / process is release.
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a systematic practice or procedure set for identifying and evaluate the potential failure modes of a process / product & its effects, and Identify actions that assessing the risks associate with these failures to eliminate or reduce the change of potential failure occurring. The results of FMEA cycle process is the FMEA Table / Risk assessment table, describe how vulnerable a product /process is to its potential failure modes and represent the level of risk attached to each potential failure mode, as well as what sufficient actions / corrective actions are require to make the change of product / process more robust.
Purpose of Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)?
- A tool used to evaluate prioritizes potential failures according to their risk and drives actions to eliminate or reduce their likelihood of occurrence.
- Provides a discipline / methodology for documenting this analysis for future use and continuous process improvement.
- Probably, an FMEA is not a problem solver, it is use to combination with other problem solving tools. The FMEA offerings the chance but does not solve the problem.
Common definitions
| KEYWORD | ABBRAVIATION |
|---|---|
| [1] Fault | Inability to function in a desired manner, or operation in an undesired manner, regardless of cause. |
| [2] Failure | As simply, Failure mean system, products / parts, assembly or function in not accordance with design commit or not meeting the specification. A mistake, fault or error owning to breakage, wear out, or compromise structural integrity. |
| [3] Failure Mode | The manner in which a fault occurs, that is the way in which the element faults. A failure mode we can consider is the manner in which a product / parts, assembly or system failure occurs. |
| [4] Failure effects | The consequences of a failure mode on a function, status, operations of a process, environment, system. The adverse consequence is cannot meet end application, poor appearance, and or the undesirable results of a fault of a system element in a particular mode. Failure effects can be harmless or fetal that equipment loss and major damage can perform. |
Why Failure Mode and Effects Analysis?
- To systematic approach for proactive risk assessment, assess the risk and results with mitigation plans.
- The FMEA provides change for identifying root causes of failure causes and implement effective corrective actions.
- The tool facilitates investigation of product / process design alternatives at all stages of the design.
- To minimize new product / process development time as well as minimize the late changes in product / process.
- To identify legal requirements compliance with new development of product.
- For define and highlight continuous improvement for the product / process by understand document the process / product related knowledge as well as it can be used as future reference.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Process Map: Table
| WHAT RESULTS (PROCESS INDICATORS) | BY WHAT? (EQUIPMENT, MATERIALS) | INPUTS | BY WHOM (PERSONAL) | HOW? | OUTPUTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of field failure mode did not identify in failure mode and effect analysis. Generally, outcomes from internal audit reporting. | To use suitable equipment and materials | Process flow chart, product / process control specification, and previous field failures of similar type of products. | Personal in charge – As Per Defined FMEA form, qualified in process / product knowledge. | Failure mode and effects analysis guidelines, manuals | Potential failure mode and effect analysis report |
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Process flow
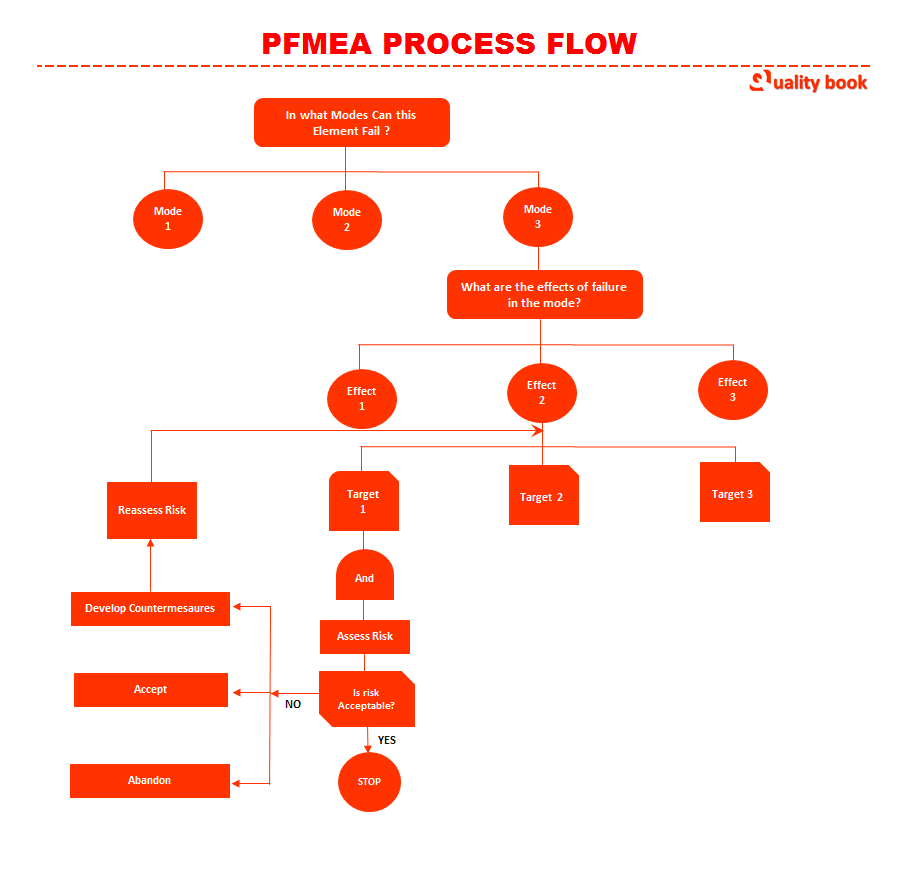
- Scope: Define the scope system as to physical boundaries, operational stages like start up, shutdown, standard run, emergency stoppage, maintenance, other rules prepared.
- Targets: identify targets to be protected, it should be personnel, product, equipment, equipment, devices and devices, productivity etc…
- Standards: identify functions, requirements and specifications, standard system accordingly.
- Risk: recognize risk tolerance limits, that can be define through risk matrix. Risk matrix must be defined for and must match the assessment probability interval and force volume.
- Failure Mode: Identify potential failure modes. Ask the question: In what way mode can this element fail?
- Root cause: Identify root cause of particular failure mode (s). Take the step-by-step in depth of the system to root cause of failure mode.
- Effects: Identify potential failure effects. Raise the question along with each failure, what are the effects? Each failure mode having its own effects or single effect of multiple failure modes.
- Control: Identify controls required to minimize risk level or eliminate possibility of failure effects.
- Risk Control: identify & prioritize risk. The identification and prioritize risk task conducted by specific or classification table to match the risk levels in process.
- Actions: Recommended actions are conduct as per identified and prioritize risk.
- Review Results: The reviews of whole results and verify any new hazards introduced, countermeasures impair system performance important to continual assessment of risks.
Type of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
There are many type of failure mode and effects analysis, but the probably used in general are (1) Design FMEA and (2) Process FMEA or Product FMEA, others are (3) system FMEA (4) Service FMEA (5) Software FMEA. Here we are talk about design & Process FMEA, but design & process FMEA is simply fit to any segment or organization that we discuss both type of FMEA.
Different between Design & process FMEA
| DETAILS | PROCESS FMEA | DESIGN FMEA |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To meet specification in drawing. Production in compliance with Drawing’s specification | To meet Target Specification. |
| Responsibility | Process Planning / Production | Design & Development |
| Objective | To avoid quality failure in process planning, production implementation. | To avoid quality failure in design & Development |
| FMEA start | After Design release. | After concept design. |
| FMEA – Period of Review | Prior to any investment | Prior to first run |
| FMEA Initial / First completion | Prior to bulk production | Prior to production release |
| FMEA End | Prior to series production | Prior to production |
Process Failure mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA)
The process failure mode and effects analysis (PFMEA) is an analytical method to ensure that potential failure mode and their associated causes have been considered and addresses.
Process failure mode and effects analysis (PFMEA) use to studying production planning risk management in manufacturing and other product realization activities is to focus the quality system control and processes with high risk.
This article (qualitybook.org) provide methods and instructions for risk analysis study using process failure mode and effect analysis (PFMEA).
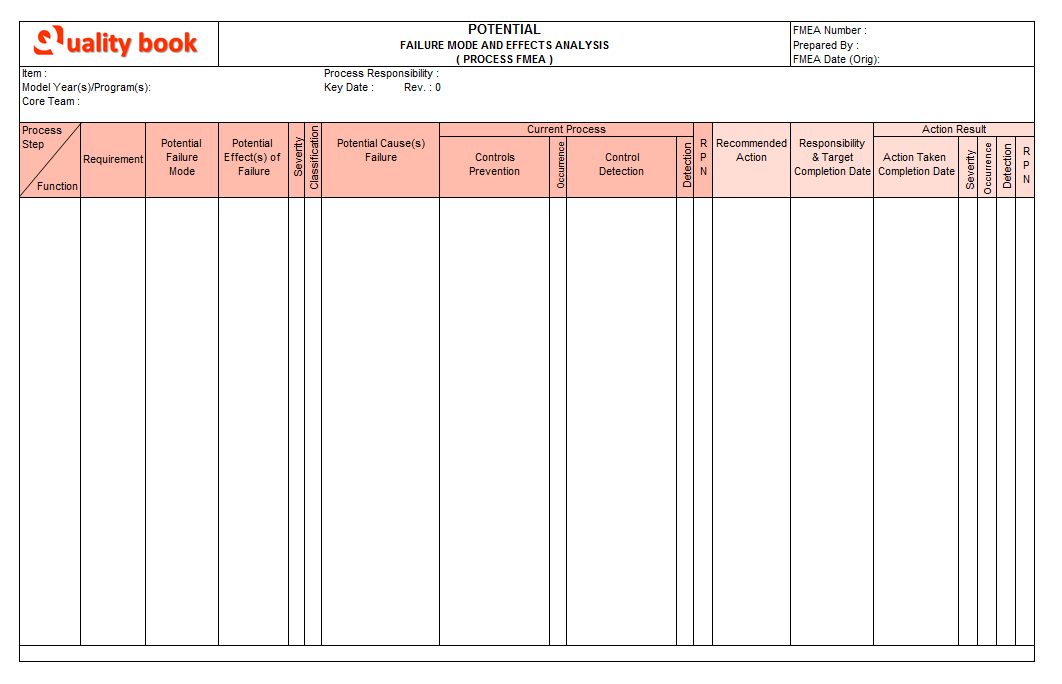
General Procedures to conduct PFMEA:
- Process function and Requirements: When we making a FMEA for particular product / process that all the details and descriptions should be specific and must first be express. The details must be easier that concern / responsible personnel can understand and ensures functions & system of product / process. Each function of the process should be specify and list outputs of the process maintain.
- The Potential failure mode: Describe how the particular part could potentially fail to execute its task. Index the failure modes those are possible to occur against the requirements specified.
- Potential effects of failure: Index the effects of failure in next operation, subsequent operations, customers and end user environment. For each failure mode, effects must be identified and indexed at in particular field, the customer (internal / external) experience with failure occurs.
- Severity: Severity is the rank associated with most serious effect for a given failure mode and it is also requiring consumer involvement while assessing the severity. For the minimize or reduce significant level of severity ranking needs to sufficient change in design. For instant ranking manage refer ranking table. Assess the seriousness of the effect in specific scale, the rating should apply to effect only and remember that the while giving ranking consider only the required criteria that is next operation.
Severity ranking Criteria Table: PFMEA
EFFECT DESCRIPTION RANK Failure to meet safety and/ or regulatory requirements (1) Major Customer Dissatisfaction (2) Cause Non-system operations (3) Non-compliance of government regulations 10 Significant Disruption, Degradation of primary functions (A) High degree of customer dissatisfaction (B) Non-functionality of system 8-9 Loss of secondary function (1) Customer Infuriating (2) deterioration of part / system performance 6-7 Annoyance / Moderate effects (A) Appearance or Auditable (B) Moderately deterioration of system performance 3-5 Minor (I) Minor natural that internal / external customer (II) probably not detect the failure 1-2 - Classification: The Classification field / column generally used to identify safety risks. It is classifying any special product characteristics and indicate the special characteristics symbol. Confirm these appearances are identified with symbol on methods and manufacturing related documents.
- Potential cause(s) of failure: Identify possible causes of each failure mode and Index all possible potential causes of failure mode like man, machine, tools, process parameters, use cause & effect diagram , index the root causes under the first level causes using why-why analysis. Generally, a potential cause should be actually initiate the failure to occur, as example the equipment setup, operator error etc. Define the causes in such a way that can be eliminated or controlled.
- Occurrence: Occurrence is the likelihood that a particular cause or failure will occur. Rank how often a particular cause is likely to consequence in the failure mode being analyzed and it should be estimated the probability of occurrence on specific scale. In case of new processes having no historical experience that use the team judgement.
Occurrence Ranking Criteria Table: PFMEA
LIKELIHOOD OF FAILURE DESCRIPTION RANK [1] Very high > 100 / 1000
> 1 in 1010 [2] High 50 / 1000
1 in 209 [3] High 20/1000
1 in 208 [4] High 10 /1000
1 in 1007 [5] Moderate 2/1000
1 in 5006 [6] Moderate 1 / 1000
1 in 20005 [7] Moderate 0.5/1000
1 in 100004 [8] Low 0.01 / 1000
1 in 1000003 [9] Low < 0.001 /1000
1 in 10000002 [10] Very low Eliminated by preventive control 1 - Current process control – Prevention and Detection: Current process control prevention is used for the methods that have been used to prevent a specific cause hence the detection field used to document methods that have been used to detect either the cause or failure mode. Index the existing controls, which can detect the causes or failure mode, while indexing specifies the frequency of detection measures.
Type of Controls
LEVEL TYPE EXAMPLES Prevention Prevention of causes Mistake Proofing Detection Detection of causes and leading to corrective action detection of defects Statistical process control, visual control etc., full inspection - Detection: Rate our capability to detect either a cause or a subsequent failure mode. Use best detection available. The rank allied with the best detection control indexed in current process control field. Assume failure had occurred and then evaluate the capabilities of controls to prevent or detect. Measure the possibility of controls indexed in the earlier field, which will detect the root or failure mode. While giving ranking.
Detection Ranking Criteria Table: PFMEA
DESCRIPTION RANK Very low (or zero) probability that the defect will be spotted. Substantiation and/or controls will not or cannot detect the existence of an insufficiency or defect. 10 Low probability that the defect will be spotted. Substantiation and/or controls not probable to detect the presence of a deficiency or defect. 8-9 Moderate probability that the defect will be spotted. Substantiation and/or controls are likely to detect the existence of a deficiency or defect. 5-7 High probability that the defect will be noticed. Confirmation and/or controls have a good chance of detecting the existence of a deficiency or defect. 3-4 Very high probability that the defect will be spotted. Substantiation and/or controls will almost certainly detect the existence of a deficiency or defect. 1-2 - Risk Priority Number (RPN): Calculate the risk priority number(RPN) is the multiplication of severity x occurrence x detection. Simply the part the failure mode severity, Failure cause probability and control detection effectiveness ratings, therefore RPN is multiple of all three above. While calculating RPN, consider only highest severity rating of each failure mode.
- Recommended Actions: Identify actions to address potential failure modes that have a high risk priority number noted. When any risk priority number identified as high needs to immediate attention of the concern since it indicates that the failure mode can consequence in a massive negative effect. It is failure source have a high probability of arising, and there are inadequate controls to catch it. So actions must be define to address failure modes that have high risk priority numbers.
Common Mistakes in Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Implementation
- Failure mode and effects analysis is not complete by a team approach. Even if it is complete, members who does not have experience in the process will be prepare part of team.
- The Failure mode and effects analysis is not completes during the design and development phase. Team tends to update after trial production is complete.
- Previous experience like a rejection, rework reports and customer complaints are not refer while conducting failure mode and effects analysis.
- Rankings are not given reliably. Many times team inclines to give lower rating to avoid initiation of actions.
- Outcomes of failure mode and effects analysis is not link effectively with the process control / design documents.
- Actually, Failure mode and effects analysis is living document, if it is consider instead as one-time activity is mistake.
- Team don’t review and update failure mode and effects analysis and related documents after every corrective action process.
Conclusion:
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a tool to identify risks in your process, it can be use in multiple places in process improvement and it is helps to determine where problems are, identify cause/ effect relationship and highlight risks in solutions and actions to take.
It is easier to identify risks to define categories like: (1) severity of impact (2) probability of occurrence and (3) ability to detect the occurrence. Generally, this tool used on early stage that is initial stage, new product / process development needs to define to understand process and identify problem areas, and analyze data to assist identification of root cause to determine best improvement with lowest risk. To the complete Failure mode and effects analysis, needs to accurate ranking for each field, see below table:
Failure mode and effects analysis(FMEA) Rankings
| SEVERITY | OCCURRENCE | DETECTION | RANKING |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazardous without warning | Very high and almost inevitable | Cannot detect or detection with very low probability. | 10 |
| Loss of primary function | High repeated failures | Remote or low chance of detection | ↑ |
| Loss of secondary function | Moderate failures | Low detection probability | ↑ |
| Minor defect | Occasional failures | Moderate detection probability | ↑ |
| No effect | Failure Unlikely | Almost certain detection | 01 |
General Process Steps:
- Describe the product or process in first field.
- Design a block diagram of the process or product.
- Complete the header details of the failure mode and effects analysis Table.
- Tally the objects (components, functions, steps, etc.) that create the product or process.
- Identify all potential Failure Modes associated with the product or process.
- Index each Failure Mode to communicate and discuss with technical term.
- Describe the effects of each of the failure modes listed and assess the severity of each of these effects.
- Identify the possible cause(s) of each failure mode.
- Quantify the probability of occurrence of each of the failure mode causes.
- Identify all current controls that contribute to the prevention of the occurrence of each of these failure mode causes.
- Determine the ability of each control in preventing or detecting the failure mode or its cause.
- Calculate the Risk Priority Numbers (RPN).
- Identify action(s) to address potential failure modes that have a high RPN.
- Implement the defined actions.
- Review the results of the actions taken and reassess the RPN’s.
- Keep the FMEA Table updated.