Since last 15 years, in manufacturing industry vast changes we can see due to awareness of system improvement, and focus on micro level management. A broader revolution of chain management impacts overall supplier chain, which makes compulsory to focus on weakness in system for any business. Due to such an arrangement, positive impacts on individual businesses and their internal system improves, which directly impacts product quality.
To establish good system, needs to initially focus on product development stage. Generally, there are two main requirement of a good product development are developing a robust product and developing it in a short time, to achieve both the objectives here on this website (qualitybook.org) we are going to discussed on such methods. One of the essential requirements for the success of this approach is the ability to work in teams. Team working is a culture which has to be developed and practiced in the organization. If we do not adhere to this principle of team working, we may end up without the benefits expected from this process of product development. So let’s discuss how to effectively implement APQP in organization.
What is APQP?
Advanced product quality planning (APQP) is consistent methodology proposed to accompanies the development of product to ensure that a product satisfies the customer’s requirements on time.
To develop and produce a new product that meets the customer’s quality requirements in directive mode, systematic advanced quality planning is needs to establish. APQP accompanies the development of a product and proposed to ensure that supplies meet all of the customer’s requirements. The Advanced product quality planning (APQP) process provides a structural method for new product introductions and modifications to existing products. It ensures that all appropriate information necessary for the successful manufacture of the specified product is taken and used to make sure that customer end applications, technical requirements as well as core requirements are understood and can be meet.
Aim to achieve:
- Effective communication with everyone involved.
- On-time completion of all required stages.
- Minimal or no quality problems.
- Minimal product launch quality risks.
- Minimal cycle time to launch the product.
With A Process:
- A. To confirm the equipment capability and capacity to meet quality requirements.
- B. To confirm the status of production preparation and finalize readiness of 4M (Man, Machine, Management, Money)
- C. To adequately establish the quality assurance and quality control system, and
- D. To maintain the quality assurance and quality control system implementation to meet the customer requirement. In carrying out this process, the product quality planning shall embody the concepts of error prevention and continual improvement as contracted with error detection and is based on multidisciplinary approach, and to monitor the performance of manufacturing processes to demonstrate compliance with customer requirements for product quality & efficiency of the process.
APQP Classification
Generally, Advanced product quality planning classifications define by the customer on based of the production process (task) having a risk involved, mostly it can be in three categories as you can see in below picture:
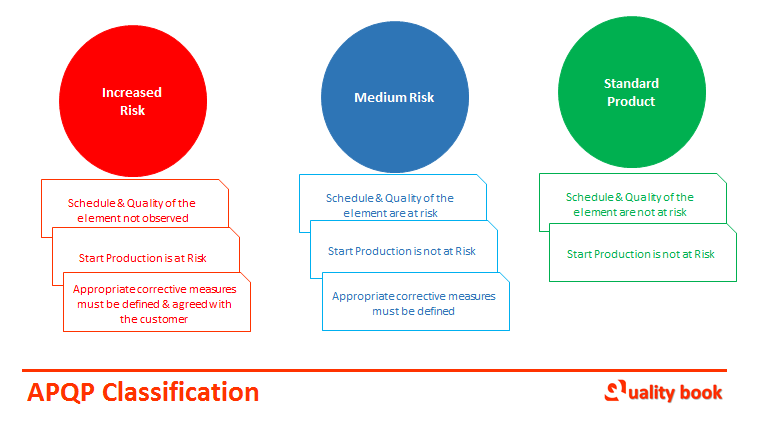
When customer issued an order to supplier, the customer define the order risk level and informed of the task classification, but it may change during ongoing task at supplier end, it creates unexpected situations, in this case supplier made changes in all the affected documents like PFMEA, Flow charts and diagrams, control plans.
Initial Risk Evaluation
The risk associated with following category, you can categorize through measure following questions with answered as present associated risk condition at workplace.
- Design Category
- New commodity for selected supplier?
- New Technology or materials?
- New or Different application of carry over part?
- New design concept?
- Are there safety / Noise Requirements / Emissions?
- Offshore Engineering site?
- Will design need to be coordinated with mating parts for fit, function or appearance?
- Are historic quality / warranty issues?
- Is program timing an issue?
- Are sample submission dates too late?
- Manufacturing category
- New Manufacturing facility?
- Is this a new manufacturing processes?
- A part or system will historical launch problems?
- Offshore manufacturing site?
- Will supplier need source evaluation?
- Is new production equipment required?
- Any potential handling or shipping issues?
- Assembly Category
- Is part installation an issue?
- Is special tool required to install / assemble parts?
- Service Category
- Is part serviceability a problem?
- Are special tools required?
Advanced product quality planning (APQP) Phases:
- Plan and define Program
- Product Design and Development
- Process Design and Development
- Product and Process Validation
- Feedback, corrective action and Continual improvement
Plan and define Program [1]
In this phase, supplier communicate with customers to understand requirements and voice of customers, and prepared team to work together to plan and define the program. The supplier learns the target of the program and prepare comprehensive plans on how they will achieve the target those program defined goals. Some possible inputs and outputs of this phase is described here as below for your reference:
Inputs:
Customer Voice: The team understand the inputs as customer voice to obtain market research to reflect the opinion of customers through conducting interviews, surveys and questionnaires as well communicate with customers through letters, emails and collect the suggestions from customers. In case of dealer management, dealer’s opinion and its comments are also considered and appreciate to improve the overall project.
Quality / Experience: Previous information of assess customer wants and the potential for recurrence concern quality data, warranty reports, capability indicators and also internal quality reports are considered for inputs to define program. Historical records and warranty details like supplier rating, problem resolution reports, FMEA and control plans are needs to considered as inputs for right direction.
Strategical Planning: Form the basis of the product quality plan, business plan needs to defines timing, cost, investment, product positioning, research and development. The planning should be covered the marketing positive strategy target customers and key sales pointes, the business plan and marketing strategy used for the inputs APQP initial phase.
Outputs:
Goals: It is important for your business to convert measureable design objectives from customer feedbacks and voices, it also needs to ensure voice of customer should not have lost the consequent design activity. Some other outputs as goal is quality goals you can measured by ppm, problem level and waste, scrap reductions percentages which indicate through matric can be good outputs measurements.
Assurance plan: To achieve or meets the program goals needs to prepare product assurance plan and ensure product & process meets program goals. According to program time setup, all the works and tasks should be properly indexed and each events and assignments are managed in chart, as well you must have considered target cost during the planning.
Objective:
To plan & Define Advanced product quality planning (APQP) for the program. To ensure that the supplier clearly understands customer needs and expectations in order to plan and define a quality program. The supplier is responsible for completing, using and updating the planning documents throughout the program.
Product Design and Development [2]
In the product design and development phase, team should follow the goal of this phase is to ensure that organization’s products and modules meet or exceed their customer’s requirements, are provided and launched as planned and that they are established in a structured and analytical manner.
Inputs:
Quality Goals: Design goals and targets are initial measurable objectives, design feasibility study is conducted as design goals and The reliability and quality targets where all the measureable reliability, warranty and incoming quality targets are considered, capability studies and six sigma implementation are conducted as inputs of the product design and development.
Initial list of special product and process characteristics includes product assurance plan. And management support involved organizational chart, initial open issues log, keep meeting minutes. The advanced product quality planning team feasibility commitment records and communication, where communicated issues related to manufacturability of the proposed design.
Outputs:
- Design failure mode and effects analysis(DFMEA)
- Reliability results
- Product special characteristics
- Product error proofing, as appropriate
- Diagnostic guidelines
- Design for manufacturing and assembly
- Design verification
- Design reviews
- Prototype build – Control plan
- Engineering drawings (including math data)
- Engineering specifications
- Material specification
- Drawing and specification changes
- New equipment tooling and facilities requirements
- Special product and process characteristics
- Gages/testing equipment requirement
- Team feasibility commitment and management support
Design & APQP outputs
| DESIGN OUTPUTS | APQP OUTPUTS |
|---|---|
| DFMEA | New Equipment, Tooling & Facilities Requirements |
| Design for manufacturability & assembly | Special Product & Process Characteristics |
| Design Verification and Design Reviews | Gauges / Testing Equipment Requirements |
| Prototype Build – Control Plan | Team Feasibility Commitment & Management Support |
| Engineering Drawings (Including Math Data) and Engineering Specifications | |
| Material Specifications | |
| Drawing & Specification Changes |
Objective:
Identify the product’s potential failure modes, assess the probability of the failure modes occurring, review the effects of such failures and formulate action plans to improve the product designs to prevent or counteract the failures and their effects.
Process Design and Development [3]
In this phase, a cooperative association must be forged between the suppliers and customer to develop a manufacturing process that will produce quality materials. To accomplish this task, the input from phases one and two are critical. Creating and developing a highly capable and productive process takes input from various resources and significant tenacity. The supplier will be interfacing with different departments, teams and facilities within customer and the output from this phase will be equally diversified.
Inputs:
- Design failure mode and effect analysis (DFMEA)
- Reliability results
- Product special characteristics
- Product error proofing, as appropriate
- Diagnostic guidelines
- Design for manufacturability and assembly
- Design verification
- Design reviews
- Prototype build-control plan
- Engineering drawings (including maths data)
- Engineering specifications
- Material specifications
- Drawing and specification changes
- New equipment tooling and facilities requirements
- Special product and process characteristics
- Gauges/testing equipment requirement
- Team feasibility commitment and management support
Outputs:
- Control Plan
- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA)
- Preventative and Predictive Maintenance Program
- Critical Spare Parts List
- Maintenance records and schedules
- Key Control Characteristics of the Product and Process
- Packaging Plan
- Logistics Plan
- Process instructions
- Accountabilities
- Packaging standards
- Product process quality system review
- Process flow chart
- Floor plan chart
- Characteristics matrix
- Process failure mode and effects analysis (PFMEA)
- Pre-launch control plan
- Process instruction
- Process approval acceptance criteria
- Measurement systems analysis plan
- Preliminary process capability study plan
- Packaging specification
- Management support
Objective:
Develop a process flow diagram and process map of layout of the manufacturing area. Develop comprehensive and effective manufacturing system to ensure the manufacturing systems meets customer requirements.
Product and Process Validation [4]
In this phase, arrangements with the essential requirements for validating the manufacturing process and product design. Manufacturing guidelines and tooling are completed in preparation for the production first trial run. An initial production run is performed to validate that the production process is capable of manufacturing product that meet the customer’s technical and end application requirements as well as capability of production requirements and design intent.
Any open issues that are identified during this phase must have actions defined with corrective action generated. The target is to have processes that are capable, meet customer’s end application requirements, material that are manufactured to as customer requirements and design intent and be able to generate an approved production part approvals (PPAP) warrant.
Inputs:
- Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
- Process Flow Charts and Process Flow Map
- Initial design drawings and specifications
- Work instructions and visual aids
- Special characteristics
- Packaging specification
- Preliminary Control Plans
- Packaging standards
- Product process quality system review
- Process flow chart
- Floor plan layout
- Characteristics matrix
- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA)
- Pre-launch control plan
- Process instruction
- Process approval acceptance criteria
- Measurement Systems Analysis Plan
- Preliminary process capability study plan
- Packaging specification
- Management support
Outputs:
- Final design drawings and specifications
- Gages, Check Fixtures, tooling, equipment
- Measurement system analysis data
- Statistical process control data
- Initial capability data
- Initial capacity data (overall equipment effectiveness)
- Final control plans
- Production Process Prove-Out Program report and parts
- Production Part Approval Process documentation
- Significant Production Run
- Measurement Systems Evaluation
- Preliminary Process Capability Study
- Production Part Approval
- Production Validation Testing
- Packaging Evaluation
- Production Control Plan
- Quality Planning Sign off & Management Support
Objective:
Validate the manufacturing processes & the product, and to ensure that customer’s requirement will be meet. The supplier shall develop a PPAP document package and submit to customer for approvals. The supplier should must communicate with customer to determine PPAP submission level requirements.
Feedback, corrective action and Continual improvement [5]
The supplier’s team prepare the plans, design, develop and validate products and processes to confirm that the program is on track concluded reviews and look for opportunities to improve. Once the product release, it is important to ensure that the program’s success and evolution into ongoing production.
The supplier must define the effectiveness of advanced product quality planning effort and includes the actual product as well as the manufacturing process to produce the product. Corrective action procedures and developed and implemented to address short term actions so future plans can get advantage.
The supplier should experience in manufacturing product, insight is obtained on how to reduce variation, waste and scrap, overall cycle time, safety requirements related and cost reduction programs.
Inputs:
- Production trial run
- Measurement systems evaluation
- Preliminary process capability study
- Production part approval
- Production validation testing
- Packaging evaluation
- Production control plan
- Quality planning sign-off and management support
- 4P Run
- Measurement Systems analysis
- Process Capability studies
- PPAP
- Product Validation testing
- Packaging evaluation
- Production Process FMEA
- Production Control Plan
- Quality Planning documentation
- Supplier ratings
- APQP Open Issues log
- Manufacturing cost information
- Equipment uptime records
- Safety records
- Customer satisfaction information, including manufacturing, assembly, owner, driver
Outputs:
- Corrective Action Plan, focusing on improvement of the product/process development cycle
- Reduced variation
- Customer satisfaction
- Delivery and service
- Continuous Improvement Plan for the actual product/process in current production
Objective:
The objective of this phase is to assess the effectiveness of APQP for the program to date and incorporate through obtain objective feedback for upcoming program planning for improve the system of planning.
Conclusion:
The advanced product quality planning (APQP) and its recommended phases used for new product development. It can apply to all products, manufacturing process and development activities & revisions in existing products / manufacturing processes like changes in product specification requirements, raw materials, or bill of materials to be used commonly.
APQP activity is carrying out for any special customer requirements received where entire manufacturing cycle need to be established. Its carrying out through five phases as describe in this article above.