A control plan is a document that fully describes the procedures required at each stage of the production process, such as quality checks or monitoring process parameters, measurement procedures, and inspections. This document is helpful in ensuring that the process outputs conform to pre-defined requirements.
This method provides support for documenting the functional elements of quality control, and ensures that the product will meet fully planned quality standards and is useful in formalizing the control system.
Control plans help in timely monitoring of all important processes and process characteristics of production areas.
Control plans are very important in the manufacturing sector because a control plan is a comprehensive document, which outlines the processes and systems. The use of which meets the specified quality and performance requirements of the product. This includes commonly used and related consumables, equipment, and personnel information as well as inspection and testing procedures.
This type of information is found in many tools, but it also includes details of the acceptance criteria for each step of the process and the process for resolving any problems that arise. Also, information on quality characteristics, training and personnel, compliance with regulations and standards, and process for continuous improvement can be included.
How exactly does it work?
- Control planning provides timely information on how to properly control quality or production areas.
- This indicates non-conformance (meaning – non-conformance of quality). An outline of actions to be taken on those non-conformity may also be included.
- The checklist can be combined with the control plan, making it easy to ensure quality inspection and process monitoring.
In fact, the control plan is a living document, which means that the control plan is updated regularly, and is amended from time to time if necessary.
What is the purpose of a control plan?
The main objectives of the control plan are as follows:
- Its main objective is to ensure that the product meets its specified quality and performance requirements through a systematic and comprehensive approach. It serves as a guide for the entire production process from raw materials to finished goods.
- To proactively identify potential problems before they arise.
- Ensuring consistency and quality in the manufacturing process.
- Control plan to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
- It also helps in identifying the resources, skills and expertise required to implement the plan and also helps in establishing a process of continuous improvement.
- Identification of critical for quality (CTQ) characteristics and monitoring and control of these characteristics throughout the manufacturing process.
- To make the company more effective in achieving its quality goals and objectives.
Why is it important to develop a control plan?
As you know one of the most challenging things in the production process is the waste generated from the production processes. So, the method development of control planning helps in reducing or eliminating the waste. Control planning plays an important role in quality improvement.
Many people ask me, what is the benefit of creating a control plan? The simple answer is that the main benefit of a control plan is that it helps identify potential problems before they occur. It provides an outline of the processes that involve all the activities as well as the equipment. So that the control plan can adopt a proactive approach to quality control, which ultimately facilitates improvement.
As we know that a control plan is a comprehensive document, which helps to ensure that the specified quality and performance requirements are met throughout the manufacturing process, from the design stages of the product to development, and from raw materials to finished goods, has been kept.
Another major benefit of a control plan is that it helps ensure consistency and quality in the production process. By providing clear guidelines and acceptance criteria for each step of the process, a control plan helps ensure that all products are produced to the same high standards. This can increase customer satisfaction and increase the good reputation of the business.
What should be included in the control plan?
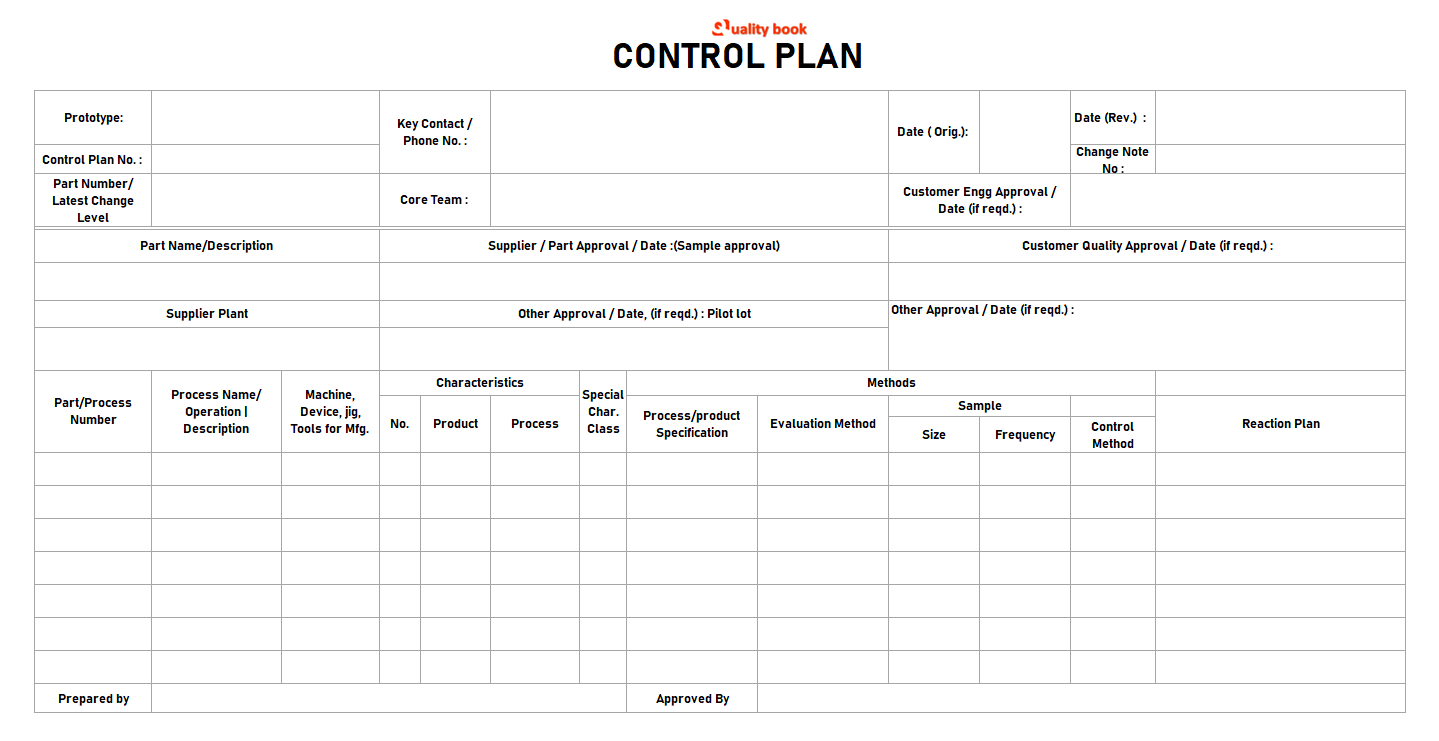
However, it is in tabular format that all the essential control plan elements are included, such as:
- Attribute important to quality: The final product attribute proves important to the customer, as well as the graded reference number.
- Significant feature number: reference number for arranging the relevant number within a hierarchy that belongs to the relevant CTQC.
- Critical characteristic description: process characteristics that have a significant impact on the quality characteristic from critical.
- Chart Types: X-Bar and R Charts, P-Charts, C-Charts, Trend Charts.
- Chart Champion: Name of the owner of the process.
- Chart Location: The location where the train is kept.
- Measurement Method: The method used to collect measurement data, e.g. Scale, caliper.
- Measurement study: To indicate whether the measurement system analysis has been completed or not. If so, show the % total error.
- Response plan: Reference number of a response plan flow-chart that tells the data-plotter what to do in the event of an out-of-control or out-of-spec condition. Condition. The response plan can be somewhat generic for families of procedures with similar schemes.
- Gauge Number: Reference number for the gauge that corresponds to the calibration tracking system.
- Sampling plan: How many samples are drawn at what frequency.
- Process Stability: Is the process under statistical control – yes or no.
- Cp/Cpk: If the process is stationary, calculate Cp and Cpk.
Elements of a Control Plan
Quality and performance are considered to be the biggest requirements for any manufacturing sector. It is therefore natural that the manufacturing sector constantly strives to create an improved product that fulfills both of these key needs. Hence a control plan is created and strives to keep quality and performance at the highest level.
A control plan is essential to ensure that it meets the specified quality and performance requirements, so its components are essential, which are as follows:
Process flow
If you want to understand how any product is made, you must first understand “What is its process flow?“. If you understand that, the rest will be understood automatically. Here, it is necessary to outline the various steps of the manufacturing process, through which we can understand where the equipment, materials, manpower, sub-processes, and testing processes used in the process are. Also, what should be the acceptance criteria for each stage of the process and the details of the process to resolve any issues that arise so that a complete control plan can be created.
Inspection and testing procedures
First, we must understand that the control plan covers all the production processes, so it also includes the processes for control. It also includes inspection and testing procedures. A control plan is a plan that meets specified quality and performance requirements, so it is necessary to detail the frequency of inspections and testing, as well as the acceptance criteria for each test.
Critical to Quality (CTQ) Characteristics
This section of the control plan identifies the critical characteristics of the product that are essential to its quality and performance. These characteristics are typically identified using quality tools such as Pareto analysis, cause and effect diagrams, and process flow diagrams. So as to understand what is required by the customers and provide them with excellent quality goods as well as complete satisfaction.
Inspection and testing equipment
When we include inspection and testing procedures, it is also necessary to indicate by which devices and equipment these procedures are completed. One thing being understood, the control plan is essential for quality and performance assurance that inspection and testing are completed in a thorough and guided manner. So that it becomes easy to confirm. This also includes calibration and maintenance of equipment as a component.
Training and personnel
If you want to ensure quality and performance through a control plan, it is essential to outline the manpower, the personnel involved in the production process, including operators, supervisors, and quality control personnel, and the training and qualifications required for them.
Continuous improvement
The question is what is continuous improvement? And what will its function be in control Plans? So, understand that continuous improvement is an activity that keeps the processes alive and ongoing, which can be understood as upgradation. This section of the control plan outlines the process for continuous improvement.
This includes the methods and techniques used to monitor and control determinants of quality characteristics and the methods used to document and report the results.
Adherence to rules and standards
Nowadays, the consumption of goods is not only local, mostly the goods are sold in every corner of the country and also in foreign countries. Obviously, as the country changes, so do its criteria, requirements, and specific rules. So, to meet the foreign requirements and related regulations of the product, it must comply with specific standards. Standards like ISO, TS, GHS etc. So here, compliance with industry specific regulations is outlined.
Overall, the control plan usually includes several key elements that are necessary to ensure that the product meets the specified quality and performance requirements.
These components include process flow, inspection, and test procedures, critical to quality characteristics, inspection and test equipment, training and personnel, continuous improvement, and compliance with regulations and standards.
By incorporating all these elements, the control plan provides a comprehensive guide to the entire manufacturing process. Also helps ensure that the end product meets and meets the desired quality and performance levels for customers.
Customer Specific Control Chart
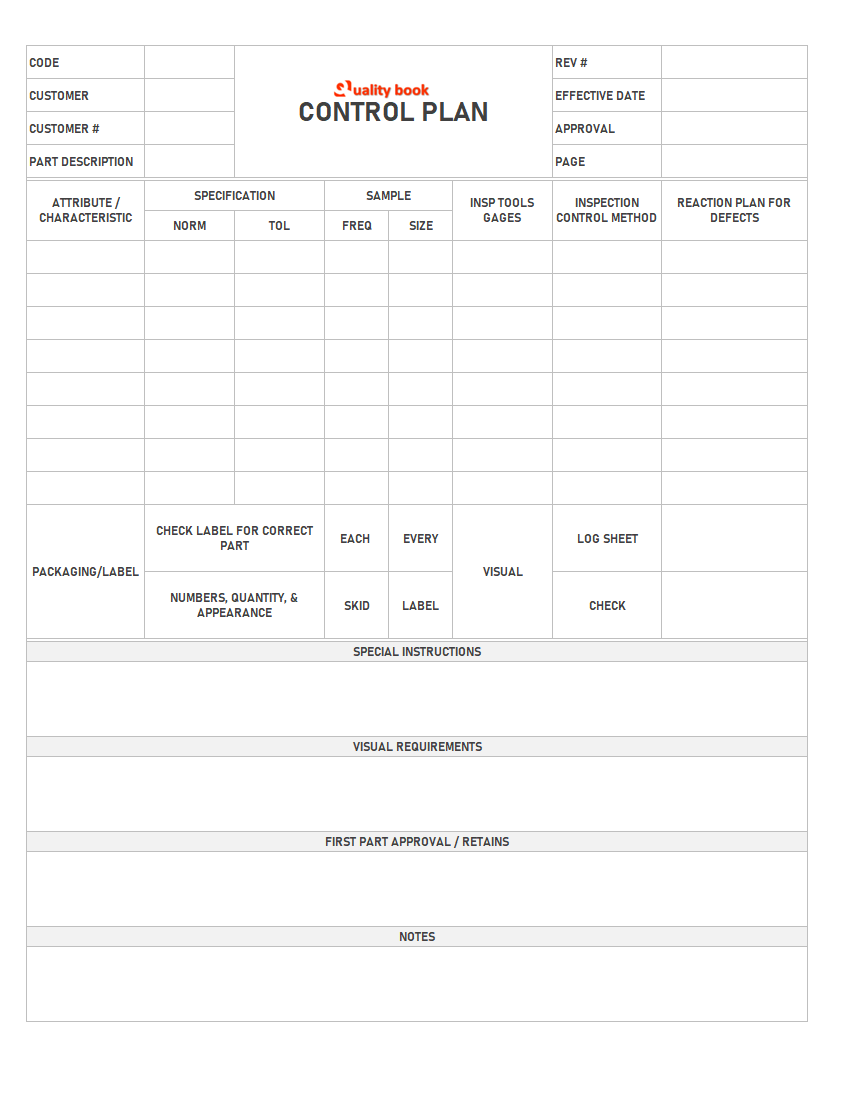
How to read the control plans?
This is a description of the information provided by the control Plan.
Code:
Code provided to the product organization. This code is for internal recording purposes and is given to the product to define the name of the customer, and the style of sheet produced for this one part.
Customer:
This is the name of the customer who ordered this part.
Customer #:
This is the number given by the customer for his/her identification purposes.
Part Description:
This is the size description of the sheet produced for this part. This is not a spec from the spec sheet.
REV#:
This is the revision number of this control Plan. Every time a control plan is updated with new information, it will get a new revision number. If this space is blank, it is the first issue of this portion control plan.
Effective Date:
This is the date this issue or revision occurs.
Approval:
This is the personnel that provides the most recent revisions. It would be the person asking if there is a quality issue or question in supervision.
Page:
Generally, a control plan is only 1 page. In some cases, there may be an attachment to the control plan that gives additional information based on customer needs or requests.
Attribute/Speciality:
This is the title directly below all the boxes. It describes the various quality aspects that should be there in the spec.
Specification:
This section gives the guidelines for each specification. At the bottom of this section, it is defined what should be the normal target for each attribute and what is the tolerance for going below or above the normal target.
Sampling:
Directly under this section is the description of how often the characteristics should be tested.
Inspection Equipment/Gauges:
Directly under this section is a description of what equipment will be used to measure each characteristic.
Response Plan for Defects:
This section instructs the operator on what to do when a spec is not met.
Special Instructions:
These are notes that are specific. If there are any special requirements included with this part, this is the area to find them.
Visual Requirements:
This section explains the visual aspects of the sheet. It covers all the specs that are not measurable.
First part approval intact:
This section instructs the operator that the quality must be maintained, tagged, and approved before any sheet can be saved.
Notes:
This section provides information that may be useful to the operator and quality inspector. This information may include such things as how the part is used or made.
General Control Chart: Sample
Conclusion
In conclusion, the control plan is an essential tool to ensure that the product meets the specified quality and performance requirements. It acts as a comprehensive guide to the entire production process and is an important tool for proactively identifying and resolving potential problems before they occur.
By outlining the procedures and processes used to manufacture a product, a control plan helps ensure consistency and quality in the manufacturing process, which in turn can lead to increased customer satisfaction and reduced costs associated with rework and defective products.
Additionally, having a control plan in place can help demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
Overall, the control plan is an important part of any quality management system and helps organizations achieve their quality goals and objectives.